The answer is no. The roller coaster is driven almost entirely by inertial gravitational and centripetal forces.
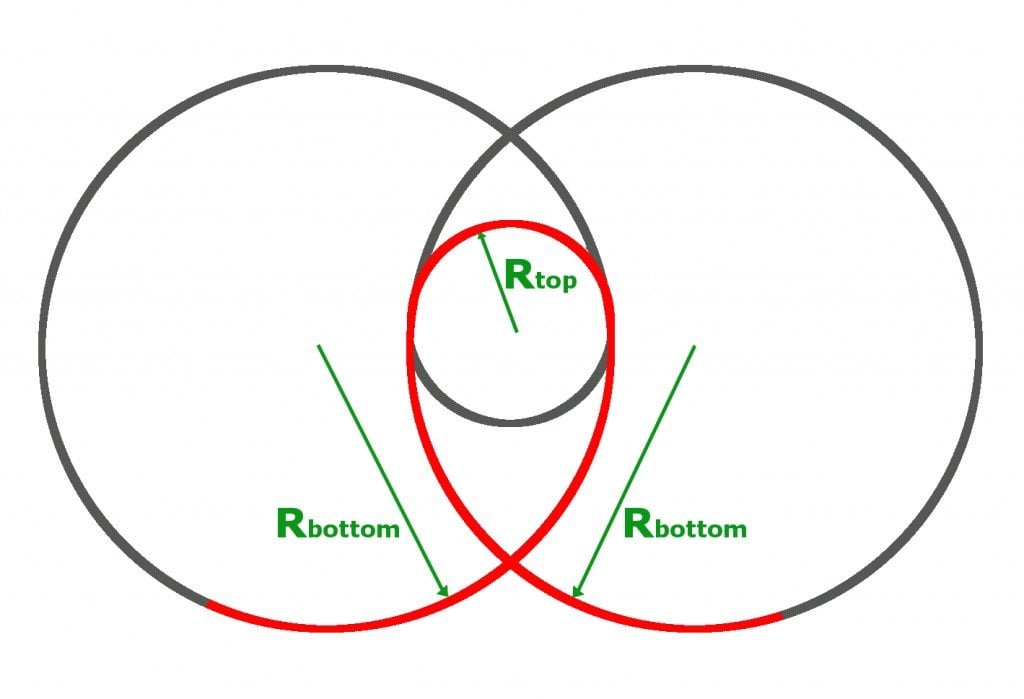 The Physics Of Roller Coasters Science Abc
The Physics Of Roller Coasters Science Abc
A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track.

Physics behind roller coasters. They now use magnetic propulsion the attraction of magnetic fields between the track and the bottom of the train. The primary force that makes one feel a particular set of sensations is the acceleration and the section of a roller coaster that exploits this acceleration more accurately known as centripetal acceleration are the clothoid loopsa clothoid loop assumes the geometric shape of a teardrop. Roller coasters may be vomit and tear inducing thrill machines but theyre also fascinating examples complex physics at work.
It mobilizes and gives its riders amusement through forces such as inertia gravitation and centripetal forces and utilizes different types of energies such as potential and kinetic energy. Roller coasters have many functions that involve electromagnets. Velocity is the speed of an object in a certain direction.
The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea. To get the marble to start moving gravity works to increase its velocity. During the associated activity students design build and analyze model roller coasters they make using foam tubing and marbles as the cars.
Roller coaster physics roller coaster physics provide a fascinating look into how roller coasters work. It creates a quick acceleration where as before roller coasters relied on an uphill chain start. Physics is what makes roller coasters safe and.
The main type of acceleration on a roller coaster is centripetal acceleration. Getting a string of cars through a knot of drops flips rolls. Students explore the physics exploited by engineers in designing todays roller coasters including potential and kinetic energy friction and gravity.
Learn about roller coaster physics and how coasters use the laws of energy. The physics behind roller coasters to understand how a roller coaster works you have to understand some of the physics behind it. Roller coasters are driven by physics.
The angle that the track is inclined at helps. When a coaster has reached the highest point along its course normally a tall hill at the beginning of the circuit gravity is what provides the force that controls the speed of the ride. This type of acceleration can produce strong g forces which can either push you into your seat or make you feel like youre going to fly out of it.
The combination of gravity and inertia along with g forces and centripetal acceleration give the body certain sensations as the coaster moves up down and around the track. The train is moved by gravity and momentum. Another important aspect of roller coaster physics is the acceleration the riders experience.
Energy Transformations On Roller Coasters Physics Behind Roller
 Roller Coaster Jpg Roller Coaster Energy Science Fair Energy
Roller Coaster Jpg Roller Coaster Energy Science Fair Energy
 Principle Of The Roller Coaster Youtube
Principle Of The Roller Coaster Youtube
 The Loop The Kinematics And Forces Of Roller Coasters
The Loop The Kinematics And Forces Of Roller Coasters
 Amazon Com Mary Catherine Makes Everything Fun A Play About The
Amazon Com Mary Catherine Makes Everything Fun A Play About The
Explaining Physics In Roller Coasters Roller Coaster Physics
 How Rollercoasters Work Science Of Rollercoasters
How Rollercoasters Work Science Of Rollercoasters
 Roller Coaster Science Thrills Chills And Physics World
Roller Coaster Science Thrills Chills And Physics World
Roller Coaster Physics Roller Coaster Physics
 The Physics Of Roller Coasters Youtube
The Physics Of Roller Coasters Youtube
 Roller Coaster Physics Study Com
Roller Coaster Physics Study Com
The Scientific Theory Behind The Coasters Roller Coaster
 Cobh Scientist The Physics Behind A Roller Coaster
Cobh Scientist The Physics Behind A Roller Coaster
 The Physics Of Roller Coasters Ryliemetter
The Physics Of Roller Coasters Ryliemetter
 Physics Of Roller Coasters Lovetoknow
Physics Of Roller Coasters Lovetoknow
 My Physics Blog Physics Behind Roller Coasters
My Physics Blog Physics Behind Roller Coasters
 Ppt Roller Coaster Physics Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Roller Coaster Physics Powerpoint Presentation Free
 The Physics Of Roller Coasters Science Abc
The Physics Of Roller Coasters Science Abc
 Roller Coaster Physics Howstuffworks
Roller Coaster Physics Howstuffworks
 Coasters 101 An Engineer S Guide To Roller Coaster Design
Coasters 101 An Engineer S Guide To Roller Coaster Design
 Roller Coaster Science Thrills Chills And Physics World
Roller Coaster Science Thrills Chills And Physics World

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar